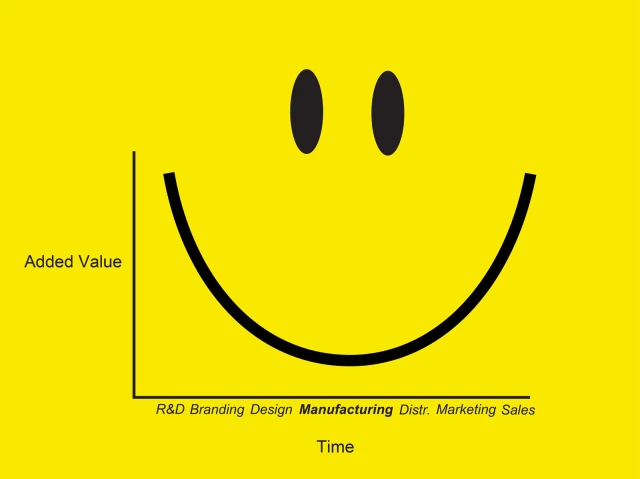
The value chain smile curve is a concept used to describe the distribution of value-adding potential across different stages of the production process in an industry. The curve illustrates that the value added by the initial stages (e.g., raw materials and basic manufacturing) and the final stages (e.g., marketing, sales, after-sales services) of the production process is higher compared to the middle stages (e.g., assembly, simple processing).
Here’s a more detailed breakdown:
- Initial Stages (High Value-Added): At the beginning of the value chain, activities such as research and development (R&D), design, and innovation are crucial. These activities require a high level of expertise, creativity, and investment, and thus, add significant value to the final product. For instance, the design of a new smartphone or the development of a new pharmaceutical drug can be very valuable.
- Middle Stages (Lower Value-Added): The middle stages of the value chain often involve manufacturing, assembly, and other forms of processing that are more routine and can be easily outsourced or automated. These activities add value but tend to be more commoditized and, therefore, capture less profit compared to the initial and final stages. The competition is fiercer here, and the differentiation is less pronounced.
- Final Stages (High Value-Added): At the end of the value chain, activities such as marketing, branding, customer service, and after-sales support play a critical role in differentiating products and services in the market. These activities require a deep understanding of consumer needs and preferences, as well as strong brand management, both of which add significant value to the product or service.
The smile curve is so named because its graphical representation looks like a smile, with the high value-added stages at the beginning and end forming the upward curves (like the ends of a smile), while the lower value-added stages in the middle form the downward curve (like the middle of a smile).
The concept of the smile curve highlights the importance of focusing on high-value-added activities in the globalized economy. It suggests that companies can achieve greater profitability and competitive advantage by excelling at the innovative and customer-facing ends of the value chain, rather than competing solely on manufacturing efficiency in the middle stages.
Table of Contents
What is the important part of the Smile Curve?
The most important parts of the Smile Curve are the high value-added activities at both ends of the curve, specifically:
- Initial Stages (Innovation and Development):
- Research and Development (R&D): This includes the innovation, design, and development of new products or services. It’s where the foundational and breakthrough ideas are generated and developed into tangible products or service concepts. R&D is crucial for creating unique features or functionalities that set a product apart in the market.
- Design and Branding: These activities involve not just the aesthetic design but also the overall user experience and brand identity. Effective design and branding can significantly enhance the perceived value of a product, enabling companies to differentiate themselves in crowded markets and build loyal customer bases.
- Final Stages (Market Interface):
- Marketing and Brand Management: These are critical for communicating the value of the product to the target audience, building brand awareness, and establishing a strong market presence. Effective marketing strategies can significantly influence consumer preferences and purchasing decisions.
- Sales and Distribution: Efficient and wide-reaching sales and distribution networks ensure that products are accessible to the intended consumers. Innovations in distribution strategies can also create value, such as direct-to-consumer models that reduce costs and enhance customer relationships.
- After-Sales Services and Support: High-quality customer service and support can greatly enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty. It includes warranties, returns, repairs, and customer assistance. For many products, especially in the technology and luxury sectors, after-sales support is a critical factor in maintaining a premium brand image.
The emphasis on these high-value-added activities stems from their potential to generate significant profits and competitive advantages. They are crucial for brand differentiation, customer loyalty, and overall market success. In contrast, the middle stages of the value chain, typically involving manufacturing and assembly, are more commoditized and often subject to intense competition and lower margins. Companies that excel in the high value-added activities at the ends of the smile curve can often command premium prices and achieve higher profitability.
Where is marketing in the Smile curve?
In the Smile Curve, marketing is positioned at the high value-added end, specifically on the right side of the curve. This placement reflects the critical role marketing plays in adding value to a product or service through brand differentiation, customer engagement, and market positioning.
Marketing activities involve:
- Brand Management: Establishing and maintaining a strong brand identity that resonates with the target audience.
- Market Research: Understanding customer needs, preferences, and trends to tailor products and marketing strategies effectively.
- Advertising and Promotion: Creating awareness and interest in the product or service through various channels, including digital media, traditional media, and experiential marketing.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Building and maintaining relationships with customers to foster loyalty and repeat business.
These marketing efforts are crucial for creating perceived value and differentiating products or services in a competitive market. By effectively communicating the unique benefits and values of a product, marketing can significantly influence consumer purchasing decisions, enabling companies to command higher prices and achieve greater market share. Thus, marketing is a key driver of profitability and competitive advantage, making it one of the most important parts of the Smile Curve.
How to do more High Value-Added works?
To focus on and increase high-value-added work, organizations or individuals need to strategize and innovate in ways that enhance their core competencies, create differentiation, and deliver greater value to their customers. Here are some strategies to do more high-value-added work:
- Invest in Research and Development (R&D):
- Prioritize innovation to develop new products, services, or processes that meet untapped customer needs or improve upon existing offerings.
- Foster a culture of continuous improvement and experimentation.
- Enhance Design and Branding:
- Invest in design thinking to improve product usability, aesthetics, and overall customer experience.
- Build a strong, recognizable brand that communicates your unique value proposition and resonates with your target audience.
- Focus on Customer Experience:
- Understand your customers deeply through research and feedback mechanisms.
- Tailor your offerings and interactions to exceed customer expectations, creating memorable experiences that foster loyalty and advocacy.
- Leverage Technology and Automation:
- Automate routine, low-value tasks to free up resources for more strategic, high-value activities.
- Adopt advanced technologies (e.g., AI, blockchain, IoT) to enhance efficiency, create new value propositions, and stay ahead of the competition.
- Develop Unique Marketing Strategies:
- Create and execute innovative marketing campaigns that effectively communicate the unique benefits of your products or services.
- Use data analytics to refine your marketing strategies and target them more effectively.
- Strengthen After-Sales Support and Services:
- Provide exceptional after-sales service to ensure customer satisfaction and repeat business.
- Offer value-added services that enhance the product experience and build long-term customer relationships.
- Cultivate Talent and Skills:
- Invest in training and development programs to enhance the skills and knowledge of your workforce, focusing on creativity, innovation, and customer service.
- Attract and retain top talent by creating a supportive and empowering work environment.
- Engage in Strategic Partnerships:
- Form alliances with other businesses to access new markets, technologies, or expertise.
- Collaborate with academic institutions, research organizations, or startups to foster innovation and gain a competitive edge.
- Optimize Supply Chain and Logistics:
- Streamline your supply chain to reduce costs and improve efficiency, allowing you to invest more in high-value-added activities.
- Implement sustainable practices to enhance your brand image and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
- Pursue Global Opportunities:
- Explore international markets to expand your customer base and tap into new sources of revenue.
- Adapt your products and marketing strategies to meet the needs and preferences of different cultural and demographic segments.
By focusing on these strategies, organizations can shift their resources and efforts towards high-value-added activities, driving growth, innovation, and long-term success.
Do the developed countries use R&D and Marketing as high-value-added works?
Yes, developed countries often emphasize Research and Development (R&D) and marketing as high-value-added activities to sustain economic growth, maintain competitive advantages, and foster innovation. These activities are crucial for companies in developed economies for several reasons:
R&D in Developed Countries:
- Innovation and Technological Leadership: Developed countries invest heavily in R&D to pioneer new technologies, products, and services. This emphasis on innovation helps companies maintain technological leadership and competitive advantages in global markets.
- Economic Growth: R&D contributes significantly to economic growth by creating new industries, enhancing productivity, and opening up new markets. Developed countries often have the financial resources, infrastructure, and skilled workforce necessary to support extensive R&D activities.
- Sustainability and Societal Challenges: R&D in developed countries is increasingly focused on addressing global challenges, such as climate change, renewable energy, and health care. Investing in research to solve these issues not only adds value to companies but also contributes to societal well-being.
Marketing in Developed Countries:
- Brand Differentiation and Value Creation: In the highly competitive markets of developed countries, marketing is essential for brand differentiation. Effective marketing strategies help companies create and communicate value to their target customers, distinguishing their products and services in saturated markets.
- Global Brand Expansion: Companies in developed countries use sophisticated marketing techniques to expand their brands globally. This includes understanding and adapting to cultural differences, leveraging digital marketing platforms, and creating global advertising campaigns.
- Customer Engagement and Loyalty: Marketing efforts in developed countries increasingly focus on building long-term relationships with customers through loyalty programs, personalized marketing, and customer engagement strategies. These efforts are designed to enhance customer lifetime value and sustain long-term revenue streams.
The Strategic Importance:
For developed countries, the focus on R&D and marketing is strategic. These high-value-added activities are pivotal for:
- Staying ahead in technological advancements and innovation.
- Sustaining high-wage economies by creating jobs that require advanced skills and education.
- Competing on a global scale, not just on price but on quality, innovation, and brand strength.
Governments in developed countries often support R&D and marketing through policies like tax incentives, grants for research, and support for export marketing to encourage these high-value-added activities. This approach underscores the recognition of R&D and marketing as essential drivers of economic prosperity, innovation, and competitive advantage in the global marketplace.
How to start R&D?
Starting Research and Development (R&D) within an organization involves a series of strategic, organizational, and operational steps. Here’s a guide to initiating an effective R&D process:
1. Define Your Objectives and Scope
- Identify Goals: Clearly define what you aim to achieve with your R&D efforts. This could include developing new products, improving existing products, or creating new services.
- Scope: Determine the scope of your R&D activities. Will you focus on technological innovation, product development, process improvement, or a combination of these areas?
2. Conduct Market and Industry Research
- Market Needs: Research to identify gaps in the market or unmet customer needs. Understanding these can help direct your R&D efforts towards areas with high demand.
- Competitive Analysis: Analyze your competitors’ strengths and weaknesses to identify opportunities for innovation and differentiation.
3. Allocate Resources
- Budget: Determine how much you can invest in R&D. Consider both direct costs (like salaries for researchers and materials) and indirect costs (such as training and infrastructure upgrades).
- Human Resources: Identify the team needed for R&D activities. This might involve hiring new talent or training existing employees with the necessary skills.
4. Build or Enhance Your R&D Infrastructure
- Facilities and Equipment: Ensure you have the necessary facilities and equipment to support R&D activities. This may include laboratories, testing equipment, and software tools.
- Technology: Leverage the latest technologies that can aid in your R&D efforts, such as AI, machine learning, or simulation software.
5. Establish a Process for Innovation
- Idea Generation: Implement mechanisms for generating ideas, such as brainstorming sessions, suggestion boxes, or innovation workshops.
- Evaluation and Prioritization: Develop criteria to evaluate and prioritize ideas based on their feasibility, potential market impact, and alignment with your strategic goals.
6. Plan for Intellectual Property (IP) Protection
- IP Strategy: Consider how you will protect the innovations resulting from your R&D activities. This may involve patents, trademarks, or keeping certain processes as trade secrets.
- Legal Guidance: Seek legal advice to understand the best ways to protect your intellectual property rights in different jurisdictions, especially if you plan to operate or sell internationally.
7. Foster a Culture of Innovation
- Encourage Creativity: Create an environment that encourages creativity and experimentation. Recognize and reward innovative ideas and failures that lead to learning.
- Continuous Learning: Promote continuous learning and knowledge sharing among team members to keep abreast of the latest trends and technologies in your field.
8. Implement Project Management Practices
- Project Planning: Use project management tools and methodologies to plan, execute, and monitor R&D projects. Set clear milestones and deliverables.
- Agile Methodologies: Consider adopting agile methodologies that allow for flexibility and rapid iteration based on feedback and testing results.
9. Measure and Evaluate Outcomes
- Performance Metrics: Establish metrics to measure the performance and impact of your R&D activities. This can include time to market, return on investment (ROI), patent filings, or product success rates.
- Feedback Loops: Create feedback mechanisms to learn from successes and failures and inform future R&D activities.
10. Seek Funding and Partnerships
- External Funding: Explore opportunities for external funding, such as government grants, venture capital, or partnerships with research institutions.
- Collaborations: Consider strategic partnerships with universities, research organizations, or other companies to share knowledge, resources, and risks.
Starting R&D is a significant endeavor that requires careful planning and commitment. However, with a clear strategy and dedicated resources, R&D can be a powerful engine for innovation, competitive advantage, and long-term success.
How to maximize the perceived value of a product?
Maximizing the perceived value of a product involves strategies and practices that enhance how customers view and value your product relative to its cost or compared to competitors. Here are key strategies to increase the perceived value:
1. Improve Product Quality
- Enhance Features: Improve or add features that are important to your target market. High-quality, useful features can significantly increase a product’s appeal.
- Superior Design: Invest in the design aspect of your product, making it more ergonomic, aesthetically pleasing, or easier to use.
2. Strengthen Brand Image
- Build a Strong Brand: A strong, positive brand image can elevate the perceived value of all its products. Use storytelling to convey your brand’s values, mission, and the quality of your products.
- Leverage Social Proof: Customer testimonials, reviews, and endorsements from trusted figures can boost your product’s credibility and perceived value.
3. Customize and Personalize
- Personalization: Offer customization options for your products, allowing customers to tailor them to their needs or preferences, which can significantly enhance perceived value.
- Customer Experience: Ensure every interaction with your company is positive. Excellent customer service and an enjoyable purchasing process can increase perceived value.
4. Employ Pricing Strategies
- Premium Pricing: Setting a higher price can, paradoxically, increase perceived value, as customers often equate price with quality. This strategy works well when combined with strong branding and high product quality.
- Psychological Pricing: Use pricing strategies that make the price more attractive, such as pricing items just below a round number (e.g., $99.99 instead of $100).
5. Offer Exceptional After-Sales Support
- Warranties and Guarantees: Offering robust warranties or satisfaction guarantees reduces the perceived risk of purchasing and can increase the product’s value in the eyes of consumers.
- Responsive Support: Ensure that customer support is easily accessible, helpful, and responsive to all queries and concerns.
6. Highlight Unique Value Proposition (UVP)
- Clear UVP: Clearly communicate what makes your product unique and why it’s the best choice for the customer. This should address specific needs or problems your target market faces.
- Focus on Benefits: Emphasize the benefits of using your product, not just its features. How does it improve the customer’s life or solve their problems?
7. Utilize Content Marketing
- Educational Content: Create content that educates your audience about your product, its uses, and its benefits. This can include blogs, videos, and tutorials.
- Storytelling: Use storytelling to connect emotionally with customers, making your product more memorable and desirable.
8. Leverage Technology and Innovation
- Innovative Solutions: Continuously seek to innovate and incorporate the latest technology into your products to stay ahead of competitors and meet evolving customer needs.
- Showcase Technological Superiority: If your product uses advanced technology or innovative processes, highlight these aspects in your marketing materials.
9. Focus on Sustainability and Ethics
- Sustainable Practices: Products that are environmentally friendly or ethically sourced can have higher perceived value, especially among conscious consumers.
- Transparency: Be open about your production processes, sourcing, and corporate social responsibility initiatives. Transparency can build trust and increase perceived value.
10. Create Scarcity and Exclusivity
- Limited Editions: Offering limited-edition products can create a sense of scarcity, making your product more desirable.
- Exclusivity: Membership programs or exclusive offers for certain customers can enhance perceived value by making customers feel part of a select group.
Implementing these strategies requires understanding your target market’s preferences and values. It’s also crucial to consistently deliver on your promises to sustain and increase the perceived value over time.
How to create competitive advantages with a Value chain smile curve?
Leveraging the Value Chain Smile Curve to create competitive advantages involves focusing on high-value-added activities at both ends of the curve—innovation and development on one end, and marketing, branding, and after-sales service on the other. Here’s how to strategically approach each segment:
1. Focus on Innovation and R&D (Left Side of the Smile Curve)
- Invest in R&D: Allocate resources to research and development to innovate new products, services, or processes. This can lead to breakthrough products or significant improvements in existing offerings.
- Embrace Technology: Adopt the latest technologies to enhance your product offerings and processes. This includes digital technologies, AI, and automation to improve efficiency and create innovative products.
- Foster a Culture of Innovation: Encourage creativity and experimentation within your organization. Reward innovative ideas and failures that provide learning opportunities.
2. Strengthen Design and Branding
- Unique Design: Invest in design to make your products not only functional but also aesthetically pleasing and user-friendly. Good design can significantly enhance perceived value.
- Brand Differentiation: Build a strong brand that stands for something meaningful to your target customers. A strong brand identity can create emotional connections and loyalty.
3. Enhance Customer Experience
- Understand Your Customers: Use market research to deeply understand your customers’ needs, preferences, and pain points. Tailor your products and services to meet these needs better than your competitors.
- Customer Service Excellence: Provide exceptional customer service before, during, and after the purchase. Responsive, helpful customer service can turn satisfied customers into loyal advocates.
4. Adopt Advanced Marketing Strategies (Right Side of the Smile Curve)
- Leverage Digital Marketing: Utilize digital marketing tools and platforms to reach your target audience more effectively and measure the impact of your marketing efforts.
- Content Marketing: Create valuable, relevant, and consistent content to attract and retain a clearly defined audience, ultimately driving profitable customer action.
- Social Proof: Use testimonials, reviews, and influencer partnerships to build trust and credibility for your brand.
5. Offer Comprehensive After-Sales Services
- Warranty and Support: Offer generous warranties and accessible, efficient after-sales support. This can differentiate your brand and build long-term loyalty.
- Customer Feedback Loop: Implement mechanisms to gather and act on customer feedback. This can inform product improvements and innovations, enhancing customer satisfaction.
6. Optimize Operational Efficiency
- While focusing on the high-value-added activities, don’t neglect the efficiency of the middle stages of the value chain. Operational efficiency in manufacturing and logistics can reduce costs and improve quality.
- Supply Chain Management: Streamline your supply chain for efficiency and sustainability. Strong relationships with suppliers can lead to cost savings and innovation.
7. Global Strategy and Local Adaptation
- Global Reach with Local Touch: If applicable, expand your market reach globally while adapting your offerings to local tastes and regulations. This can open up new markets and revenue streams.
8. Continuous Improvement
- Lean and Agile Methodologies: Implement lean and agile methodologies in product development and operations to continuously improve and adapt quickly to market changes.
9. Strategic Partnerships and Collaborations
- Collaborate: Form strategic partnerships with other companies, research institutions, or universities to share knowledge, resources, and access to markets.
By focusing on these high-value-added activities and continuously seeking ways to innovate and meet customer needs, companies can create sustainable competitive advantages. The key is to not only excel in innovation and marketing but also ensure that the entire value chain is optimized for efficiency and responsiveness to market demands.